
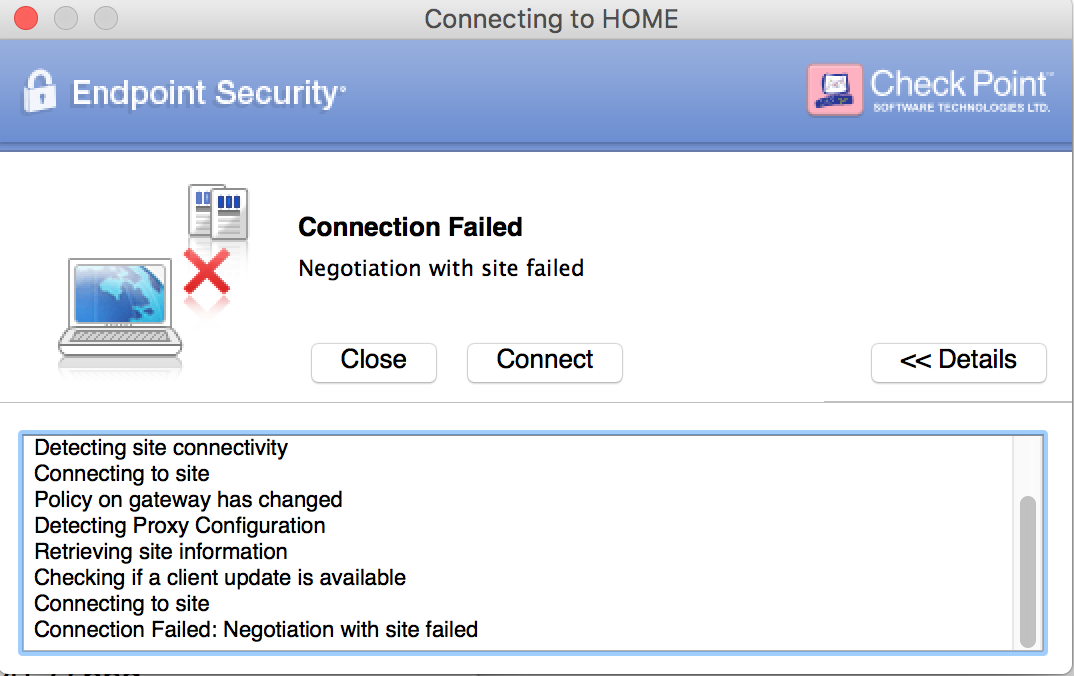
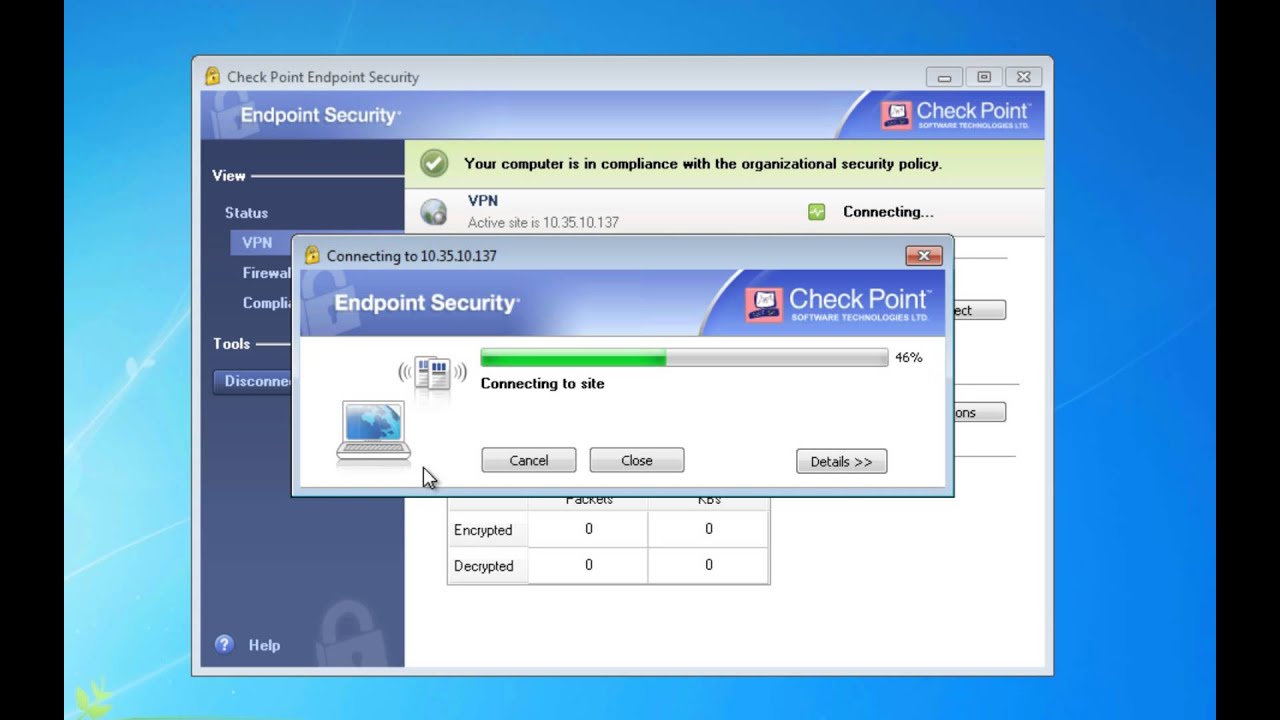
Subsequent tutorials in this series will explain how to install and run WireGuard on Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS systems and devices. You’ll also learn how to route the peer’s Internet traffic through the WireGuard server in a gateway configuration, in addition to using the VPN for an encrypted peer-to-peer tunnel.įor the purposes of this tutorial, we’ll configure another Ubuntu 22.04 system as the peer (also referred to as client) to the WireGuard Server. In this tutorial, you will set up WireGuard on an Ubuntu 22.04 server, and then configure another machine to connect to it as a peer using both IPv4 and IPv6 connections (commonly referred to as a dual stack connection). Different versions of TLS include support for hundreds of different cryptographic suites and algorithms, and while this allows for great flexibility to support different clients, it also makes configuring a VPN that uses TLS more time consuming, complex, and error prone. In comparison, other VPN software such as OpenVPN and IPSec use Transport Layer Security (TLS) and certificates to authenticate and establish encrypted tunnels between systems. Each version of WireGuard uses a specific cryptographic cipher suite to ensure simplicity, security, and compatibility with peers. WireGuard’s encryption relies on public and private keys for peers to establish an encrypted tunnel between themselves. It gives you the freedom to access the internet safely and securely from your smartphone or laptop when connected to an untrusted network, like the WiFi at a hotel or coffee shop. A VPN allows you to traverse untrusted networks as if you were on a private network. WireGuard is a lightweight Virtual Private Network (VPN) that supports IPv4 and IPv6 connections.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
